Data Analysis for Audit
Introduction
Auditing large financial spreadsheets for errors and inconsistencies is time‑consuming and prone to oversight. This use case explores how an AI chatbot helped identify suspicious rate outliers and other anomalies in a multi‑thousand‑row purchase register.
Procedure
A Purchase Register was exported from Tally software of a client and uploaded to Chat GPT to use our audit procedures.
Source Data: Purchase Register in Excel Format
AI Tool: Chat GPT – Model o5 thinking
Additional Tool: ICAI AASB GPT (for better sampling and reporting if required)
Why o5 thinking?
For better visual reasoning. Visual Reasoning is the process of using visual information, to think logically and draw conclusions.
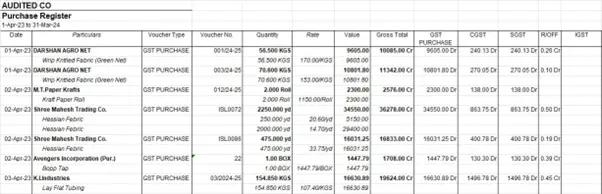
As you observe, the names of the inventory are right below the names of the parties from whom goods are purchased. Also, some columns containing numbers are actually in text format. Hence a visual reasoning model is better suited for analysis.
Prompt
(Kindly note that since we used ICAI's audit related GPT, we really didn't need to follow prompt engineering norms suggested by OpenAI.)
Output
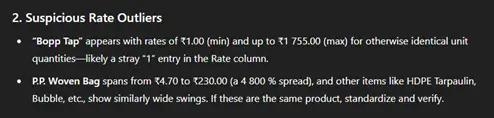
One important anomaly that was provided by the GPT was:
Industry analysis from an investment perspective
Introduction
The sugar industry, known for its cyclical nature and deep entanglement with agricultural and regulatory variables, presents unique challenges for investors. With the government frequently intervening on pricing, exports, and ethanol production, understanding the right entry and exit points becomes complex. In this context, an AI-powered financial analysis assistant was engaged to assess the sugar industry's investment potential and quality companies.
Procedure
An industry, say Sugar industry, was selected for analysis.
AI Tool: Chat GPT – Model 4.1 mini (For faster analysis)
Additional Tool: ICAI Sugar Industry AI GPT (for knowledge bank)
Prompts
Output
Summarised Answer:
1. Investment Nature of the Sugar Sector
The AI highlighted that the sugar sector is:
- Highly cyclical and seasonal, impacted by monsoons and cane availability.
- Government-driven, with interventions affecting prices and margins.
- Diversification-driven, with many players expanding into ethanol, co-gen power, and allied food businesses.
2. Timing Entry and Exit
Based on historical and current data, the AI provided a tactical guide:
- Entry Points: Before monsoon season, when ethanol policies are announced, or when global prices spike.
- Exit Points: Upon export bans, FRP increases without matching MSP hikes, or signs of overproduction.
3. Ethanol Powerhouses Identified
The AI identified companies with aggressive or strategic ethanol ventures: Dhampur Sugar Mills Ltd, Bannari Amman Sugars Ltd, Parvati Sweetners and Power Ltd, Avadh Sugar & Energy Ltd and Magadh Sugar & Energy Ltd
These players benefit from higher-margin ethanol production and align with India's E20 blending roadmap.
Prompt Engineering
Before moving ahead with our next use case, let us understand the art of asking questions – "Prompt Engineering". A good prompt may have the following 4 parts:
- Identity: Describe the purpose, communication style, and high-level goals of the assistant.
- Instructions: Provide guidance to the AI on how to generate the response you want. What rules should it follow? What should the model do, and what should the model never do?
- Examples: Provide examples of possible inputs, along with the desired output from the model.
- Context: Give the model any additional information it might need to generate a response, like private/proprietary data outside its training data, or any other data you know will be particularly relevant. This content is usually best positioned near the end of your prompt, as you may include different context for different generation requests.
Sample:
Learning any New Tool
Introduction
There is always this reluctance or hesitation whenever any new software/tool is to be used. Here we take the example of an RPA tool – Microsoft Power Automate Desktop. It automates daily monotonous tasks which erstwhile a human may be mindlessly doing. In this case for ease of discussion, we'll be taking up login to GST portal for multiple clients.
Procedure
To automate the GST login process for each client listed in an Excel spreadsheet, allowing for faster access and reduced manual intervention—freeing up time for more value-added tasks.
AI Tool: Chat GPT – Model 4o
Additional Tool: Prompt Genie (for actually creating an engineered prompt) https://www.prompt-genie.com/
Additional Tool: Google AI Studio (for visual guidance) https://aistudio.google.com/live
In Prompt Genie, we can give our requirement and it'll give a structured prompt which we can then paste to any AI tool like Chat-GPT.
Google AI Studio works like your on-site IT team, which will be observing your screen and wherever you are stuck, will guide you, just that you have to ask (literally yes!) in English.
Engineered Prompt
Prompt for Power Automate Flow Creation:
Output
Here is a clear, structured, step-by-step guide for Power Automate Desktop (PAD) to automate logging into the GST website for multiple clients using credentials from Excel.
1️⃣ Overview of the Task
You will automate logging into the GST portal for multiple clients, using User IDs and Passwords stored in an Excel file. The flow will:
✅ Open the GST login page
✅ Read each client's User ID and Password from Excel
✅ Enter these into the login fields
✅ Submit the login form
✅ Optionally, capture screenshots or status for logging/auditing.
2️⃣ Requirements
✅ Access to Microsoft Power Automate Desktop (PAD) installed on your PC.
✅ Excel file saved locally containing:
- Client Name (Column A)
- User ID (Column B)
- Password (Column C)
✅ GST Login Page URL: https://services.gst.gov.in/services/login
✅ GST login credentials are currently stored in plain text; consider encryption options if desired.
✅ Google Chrome or Microsoft Edge with PAD Web Recorder Extension installed.
3️⃣ Creating the Flow
Step 1: Create a new PAD flow
- Open Power Automate Desktop.
- Click + New Flow.
- Name it GST Login Automation and click Create.
Step 2: Add Trigger
PAD flows run manually by default, so no additional trigger is required unless you plan to schedule using PAD + Power Automate Cloud later.
Step 3: Read Excel Data
- Use Launch Excel action:
- Select: Launch Excel → Check Launch Excel with a blank document → Uncheck Visible for headless mode (or check for debugging).
- Add Open Workbook action:
- File path: path to your GST clients Excel file.
- Add Read from Excel worksheet:
- Retrieve entire table into a DataTable variable (e.g., ClientsTable).
- Set Retrieve → Values from worksheet.
- Specify range (e.g., A1:C100) or leave blank to read full data.
Step 4: Loop Through Each Client
- Use For Each action:
- For Each CurrentItem in ClientsTable
- Inside the loop, extract values:
- ClientName = CurrentItem[0]
- UserID = CurrentItem[1]
- Password = CurrentItem[2]
Step 5: Launch Browser and Navigate to GST Login
- Use Launch Chrome or Launch Edge action.
- URL: https://services.gst.gov.in/services/login
- Store the browser instance in BrowserInstance.
Step 6: Fill in User ID and Password
- Use Populate Text Field on Web Page:
- Attach to BrowserInstance.
- Use Web Recorder or UI Selector to select the User ID field, populate with %UserID%.
- Similarly, add Populate Text Field on Web Page for the Password field, populate with %Password%.
Step 7: Submit the Login Form
- Use Click on Web Page:
- Attach to BrowserInstance.
- Select the Login/Submit button.
- Optional: Add Wait for Web Page Content to ensure the page loads completely before proceeding.
- Take a Screenshot for logging using Take Screenshot action.
- Store screenshots in a designated folder named using ClientName and timestamp for documentation.
Step 8: Handle Errors
- Wrap the inner loop steps in 'Begin Error Handling'.
- On error:
- Log the client name and error message to a CSV/Excel file.
- Optionally retry once or continue to the next client.
Step 9: Close Browser and Excel
After the loop:
- Use Close Web Browser to close the GST login page.
- Use Close Excel with Save document = No.
4️⃣ Testing the Flow
✅ Start with only one or two clients in the Excel to debug.
✅ Run the flow and watch:
- Whether the correct credentials are filled.
- Whether the login is successful.
- Whether any CAPTCHA or OTP appears (requires manual intervention unless solved).
✅ Troubleshooting:
- Ensure correct selectors in the web recorder for consistent field identification.
- Use delays (Wait actions) if the page loads slowly.
- Test with different browsers if one fails consistently.
5️⃣ Best Practices
- Store sensitive credentials in encrypted format if possible.
- Use environment variables for file paths to make the flow portable.
- Implement comprehensive error logging for audit trail.
- Schedule regular maintenance checks.
- Update selectors if the GST portal updates its structure.
- Periodically validate credentials in the Excel file to avoid repeated failures.
📂 Sample Excel File
Here is a sample structure for your GSTClients.xlsx:
| Client Name | User ID | Password |
|---|---|---|
| ABC Traders | abc1234 | pwd@123 |
| XYZ Pvt Ltd | xyz5678 | pass@456 |
✅ Summary
Using this PAD flow, you will be able to automate GST login for multiple clients from your Excel file efficiently, saving time and manual effort.
Thankyou!
